Pre-translation
Pre-translation fills untranslated strings in bulk using translation memory (TM) and machine translation (MT), helping you create an initial draft that can then be reviewed and refined.
If you’ve translated common UI strings before, pre-translation can insert them again automatically (such as “Next”, “Previous”, “Cancel”), so you don’t have to type them again in every file.
Running pre-translation
Section titled “Running pre-translation”Pre-translation is run using a dedicated window, where you choose which sources Poedit uses and how the results are handled.
- Open your translation file in Poedit.
- Select the strings you want to pre-translate, or leave everything unselected to apply it to the whole file.
- Choose Translation → Pre-translate… from the menu, or click the Pre-translate toolbar button.
- Review and select the options in the Pre-translate window.
- Click Pre-translate.
- Review any entries marked as Needs Work.
Pre-translation results may be imperfect and should always be reviewed before finalizing translations.
Settings
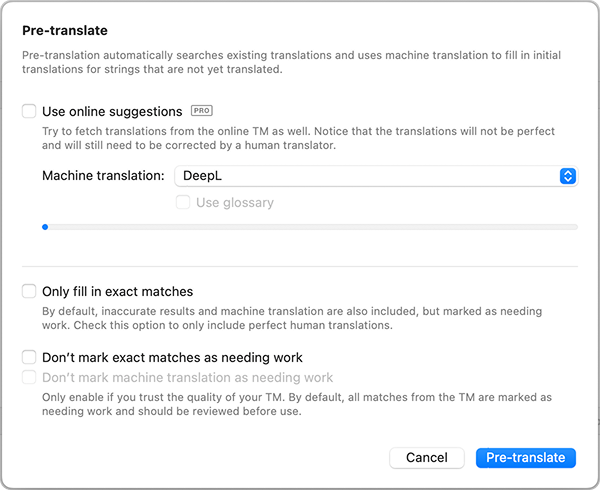
Section titled “Settings”The Pre-translate window lets you control which sources are used and how the results are treated.
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Translation Memory | Your local TM is considered and provides exact or approximate matches based on past translations. For details, see the Translation Memory documentation. |
| Machine translation | Uses a MT provider to generate draft translations for untranslated strings. MT results are always marked as Needs Work. See below for details about supported providers and options. |
| Online suggestions | When enabled, Poedit can fetch human translations contributed by other users. These work similarly to your local TM and extend it with additional exact or approximate matches. Only high-quality human translations are used. |
Machine translation
Section titled “Machine translation”When machine translation is enabled in the Pre-translate window, Poedit generates translations for untranslated strings using a machine translation provider. Machine translation is intended to help produce an initial draft that you then review and refine.
Supported providers
Section titled “Supported providers”Poedit supports multiple machine translation providers, such as DeepL, Google Translate, and Microsoft Translator. Provider availability and language support depend on your Poedit version and the language you’re translating.
Provider-specific options
Section titled “Provider-specific options”Depending on the provider and language, additional options may be available during pre-translation, such as glossaries or formality settings.
Glossaries (DeepL) If you have a glossary configured in Poedit, Poedit can pass it to DeepL so translations use consistent terminology. See the glossary documentation for details.
Formality (DeepL, selected languages) For some languages, DeepL allows you to choose a formality level (automatic, formal or informal). For details on how DeepL defines these options, refer to DeepL’s documentation.
Using your own DeepL API key
Section titled “Using your own DeepL API key”You can optionally provide your own DeepL API key. If you do, Poedit will use it for machine translation and Poedit’s machine translation quota will not apply. You can set the key in Settings → TM → Change settings or in the manage.poedit.net portal.
Exact vs inexact matches
Section titled “Exact vs inexact matches”Poedit distinguishes between exact and inexact matches when running pre-translation.
- Exact matches are translations from your TM where the source text matches exactly.
- Inexact matches include approximate TM matches, MT results, and online suggestions.
If you limit pre-translation to exact matches, Poedit inserts only exact Translation Memory matches and skips all inexact results.
Review marking
Section titled “Review marking”By default, translations inserted by pre-translation are marked as Needs Work. Some settings in the Pre-translate window let you change how exact matches are marked.
Applying pre-translation on existing translations
Section titled “Applying pre-translation on existing translations”Pre-translation does not overwrite existing translations. If you want to re-run pre-translation over strings that already have translations:
- Select the strings (or select all).
- Use Edit → Clear Translation.
- Run Translation → Pre-translate… again.
This is useful if you want to start over with a new translation approach or reapply consistent terminology from your Translation Memory.
Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”My already translated strings weren’t changed by pre-translation
Pre-translation does not overwrite existing translations. If you want to apply pre-translation to strings that already have translations, you must clear them first.
Pre-translation didn’t insert anything
This can happen if no matching translations are available in the enabled sources, or if pre-translation is limited to exact matches and no exact matches exist. Confirm at least one source is enabled in the Pre-translate window.
Pre-translation can’t run because source text is missing
If your file uses symbolic IDs instead of source text, pre-translation can’t be run. Follow the steps in the Symbolic IDs guide to resolve this.